Overview
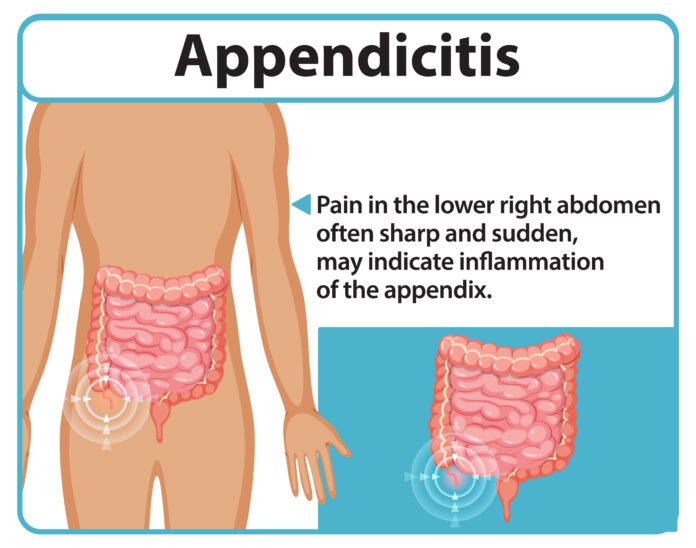
An inflamed appendix which causes intense, acute and sudden pain in your lower abdomen is known as Appendicitis. The appendix is actually a small tube-like sac located at the lower right end of your large intestine and is about the size of a finger. Sometimes, it happens that feces passing through your large intestine block your appendix tube and cause infection in it. The infection further ends in inflammation that causes swelling in your appendix. Swelling leads to bursting of appendix that known as medical emergency. Appendix bursting spreads bacteria from your bowels to all around your abdominal cavity. This causes a specific infection called peritonitis. The infection affects your bloodstream and leads to life-threatening complications known as sepsis. That’s why medical professionals recommend and prefer the removal of the appendix as the best treatment of appendicitis because the appendix located in your body is not an essential organ. The removal of the appendix is known as appendectomy.
Difference between Acute Appendicitis and Chronic Appendicitis
Acute appendicitis is a very common condition. It usually begins suddenly and worsens quickly. Most of the cases dealt as appendix belong to acute type.
While chronic appendicitis is not so common because doctors do not find many cases of chronic type. Its cause is the irritation appearing to your appendix due to something. It causes discomfort on and off but never gets worse.
Therefore, chronic appendicitis often goes unnoticed as its symptoms do not appear clearly and never escalate the way they do in acute type. However, ignoring any type of appendicitis can be harmful for your health. So whenever you experience a sudden abdominal pain and don’t know the actual cause of it, visit your healthcare provider for a proper checkup. Maybe it belongs to the appendix. Because it is observed many times that chronic appendicitis turns into acute and causes serious complications. Therefore, healthcare orders treat both types on an immediate basis.
Is Appendicitis Common?
Strides show that in children and teens appendicitis is more common than adults. This means the risk of developing the condition is higher during the age between 12 to 30.
According to a survey, around 10% of the teen population is affected by appendicitis in the country. It is ranked as the leading cause of abdominal pain in younger children leading to emergency surgery of the abdominal cavity.
However, the rate of chronic appendicitis is lower than acute type.
Symptoms and Signs of Appendicitis
Loss of appetite, abdominal pain and nausea are recognized as the common symptoms of appendicitis whether it is acute or chronic. The typical way of occurring these symptoms make it easy to recognize them as signs of appendicitis. However, it is a matter of worry that more than half of appendicitis patients do not have classic presentation of symptoms that can make the diagnosis possible.
Moreover, the typical symptoms of the condition do not appear in young adults, children and pregnant women at all.
Early Signs of Appendicitis
As an early sign, the abdominal pain starts suddenly and it surrounds your belly gradually. It is sometimes persistent and often it comes and goes for several hours. After some time,the pain becomes intense and symptoms of nausea and vomiting start to develop.
If left injured, after a few hours pain shifts to the right part of the lower abdomen toward the appendix and nausea passes. It is the time when pain gets worse and puts more discomfort in the area.
Additional Symptoms Of Appendicitis
Other possible symptoms of condition may include:
Swollen Belly: Appendicitis makes your belly distended and it looks like a bloated one. This is considered as an advanced symptom and usually shows the rupturing of your appendix tube.
Diarrhea: It can cause overactive bowels and frequent poops in some people. This actually happens due to discomfort that disturbs the end portion of the colon and makes it inflamed.
Fever: More than half percentage of appendix patients develop a fever when they get affected by appendicitis. The cruise unit temperature indicates that infection is spreading and inflammation is increasing. This is because your immune system starts to kick into a high gear.
Urinary Symptoms: You start feeling a frequent urge to pee. This is because appendicitis has started to irritate the nerves connected to your bladder and intestines.
Malaise: A feeling of being unwell always makes you dull. You always prefer to lay in bed due to lack of energy and motivation.
Bowel Paralysis: Sometimes, your bowels stop temporarily due to resurrection of blood flow from your bowel to your appendix, this leads to constipation and develops a feeling of not being able to pass gas. You may also start feeling that a smooth bowel movement can help ease the symptoms.
What Other Conditions might be Confused with Appendicitis?
Many other health conditions also have symptoms similar to appendicitis. Especially in females it happens because in female bodies, the lower abdomen lies near to their pelvic cavity. The conditions affecting their pelvic cavity are often similar to appendicitis. The organs affected by these symptoms include phenotypic system and urinary system.
More possible conditions that might be confused with appendicitis include:
- Kidney stone.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Endometriosis.ovarian cyst.
- Gastroenteritis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Urinary tract infection.
- Diverticulitis of the colon.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases.
Causes of Appendicitis
Your appendix is located at a place where it can be easily clogged or blocked by some infectious matter. The large intestine is located near your appendix that is a hive of bacteria. These bacteria enter your appendix and make it infected. The overgrowth of bacteria in the appendix makes it painful and irritating.
However, it is not always primary, infection sometimes is secondary. This means the appendix doesn’t always begin with infection. It can be swelling in your appendix that closes the opening of and traps more bacteria in it.
The causes of inflammation, infection, swelling and obstruction in your appendix may be:
Colitis: Inflammatory bowel disease or some other infections cause inflammation in your colon. The spreading of infection inflammation leads to appendicitis.
Hardened Poop: Calcified feces also known as appendicitis. The hardened poo gets stuck in the opening of your apartment and also carries and traps bacteria there. This leads to appendicitis.
Lymphoid Hyperplasia: Your immune system has an association with your lymphatic system. Both work together to fight against infections by producing and releasing white blood cells into your tissues and bloodstream. These swollen tissues obstruct the appendix and cause an infection leading to appendicitis.
Opening of appendix can also be blocked by:
- Cystic fibrous.
- Tumors.
- Parasites.
What Causes Chronic Appendicitis?
It usually starts with a mild inflammation that gets on and off for a long time. But the overgrowth of bacteria and developing symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease can also cause chronic type.
In addition, an obstruction in the opening of the appendix can also lead to chronic appendicitis as well.
Moreover, lymphoid hyperplasia is another cause of inflammation or even scars in your appointment that last for a very long time.
Is Appendix Genetic?
Appendix is not a hereditary disease. If you have a family history with appendicitis, it never poses a risk of developing the symptoms in you. This means the condition cannot be inherited but genetics may be involved in causing inflammation to some extent.
Possible Complications Related to Appendicitis
Very serious complications can occur when you have appendicitis. That’s why healthcare providers always recommend emergency treatment for it. Its compilations on it show up similar to all but they progress instead.
The stages of complications include:
Necrosis and Ischemia: When the swelling increases and becomes unbearable it cuts out blood up to the appendix, the phenomenon is an ischemia that often leads to decay of appendix tissues known as cell death or necrosis.
Perforation or Gangrene: Necrosis spreads throughout the tube and causes a severe infection. It can cause a quick burst of appendix that is known as perforation or spreads slowly through internal gangrene.
Abscess: The infection, initially, does not spread beyond your appendix and might form an abscess, known as a packet filled with pus located on the outside of your appendix. This is an infectious mass that can burst any time.
Peritonitis: The infection starts spreading to your peritoneal cavity and makes it infected. The condition is called peritonitis. This can make your bloodstream and even trans-infect. The infectious bloodstream can lead to septic shock or sepsis that proves fatal in many cases.
Diagnosis of Appendix
Appendix diagnosis involves a session of complete discussion between you and your healthcare provider about the pain and other symptoms you’re experiencing. They perform thorough physical tests to check physical signs of appendicitis after completing the question about symptoms. They may check the stiffening, guarding and pain in the appendix after applying a pressure. Your typical profile of symptoms help them diagnose the condition right away. If you don’t have one, they proceed with further tests to complete the diagnosis procedure.
Common tests performed to diagnose the appendicitis include:
- Imaging tests.
- Blood tests.
- Abdominal ultrasound.
- High white blood cell count.
- C T scan.
- C-creative protein count.
Sometimes, your healthcare provider may order additional tests to rule out other conditions.
Treatment and Management
Appendicitis treatment is not obvious. In some cases it resolve itself spontaneously when the cause goes away on its own. It happens when obstruction in your appendix passes on through your intestine or an infection that has caused lymphoid hyperplasia in your appendix suddenly improves itself. But when the pain doesn’t reduce and symptoms get worse, you need medical emergency treatment.
Therefore, doctors have declared it as an emergency. This is treated in the emergency ward. The treatment options for appendicitis include:
Medications
Antibiotics are considered good for treating appendicitis in early stages. They are the standard preventive measure before surgical treatment that can be started even when you don’t have an infection.
The very early or mild cases of appendicitis are usually dealt with as a wait and watch approach. Your doctors wait if your condition improves with antibiotics only. People have risk factors that make surgery less safe than usually offered medication.
However, healthcare providers rarely recommend this option because appendicitis often comes back when it is left untreated. Medications , no doubt, can help you to relieve pain.
Surgery
An inflamed appendix can rupture or burst within 40 hours. This is dangerous and life-threatening. So, once you are diagnosed with appendicitis, go for surgical treatment immediately. Your doctor may schedule your appendectomy within 24 hours of your diagnosis. This is the most common surgical treatment option performed worldwide for the removal of infected appendix.
However, surgeons sometimes prefer to perform a minimally invasive method, known as laparoscopy.
In addition, the complications during surgery are also treated with medications. Your abdomen is usually rinsed with a sterile solution after surgery to avoid any complication related to surgery.
Moreover, removal of the appendix is not linked with any side effect. Doctors strongly agree with the hypothesis that your appendix has no function in your body. Some theories say that in early childhood, it just functions to produce some antibodies.
What is the Recovery Time after Appendectomy?
A simple appendectomy doesn’t need a long rest. You can go home same day after having surgical removal of the appendix. However, if you had an open surgery or experienced some complications from appendectomy, your doctor may recommend you to stay in the hospital under observation of professional healthcare order a little longer. You might need pain killers during a furious few days after surgery. However, people get full after appendectomy within 7 to 8 days maximum.
Conclusion
The appendix is the non-functional organ in your body. It is located in the lower abdominal cavity. You just notice it when it starts hurting due to some triggers like infection, inflammation or clogging if it’s opening. It is good to head to the hospital right after you experience any discomfort, irritation or pain in your appendix. These symptoms indicate the appendicitis that might cause bursting of appendix, leading to death.
In rare cases, the condition is cured with antibiotics but in most cases the removal of the appendix through surgery is the only treatment option for appendicitis. Once it is removed successfully, you will never have to worry about it again.