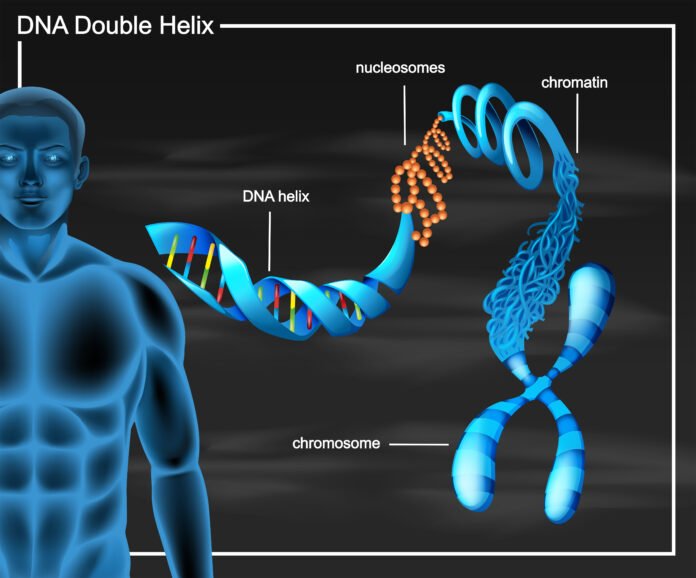
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid (DNA) is the molecule having all the instructions about your life in encoded form. Every cell of the human body contains its DNA that decides the necessary factors to maintain its life. The basic chemical substances found in DNA molecules are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. These basic substances combine together in a specific manner to form a strand of DNA molecule. The DNA molecules have specific fragments located on them, known as genes which are responsible for having important information necessary to formulate proteins that are essential for perfect functioning of all cells of the human body.
Genetic material composed of a complete set of DNA, is known as the genome. The complete genome pattern is found in every cell of your body. You can assume it as a single long strand of DNA that is crossing from all cells of your body. But this is not simple as the DNA molecule has been divided into countless unequal segments and coveted in a compact form known as chromatin.
DNA, genes and chromosomes are collectively called your genetics. Genetics play a crucial role in maintaining your health. The genes in your cells actually are responsible for dictating how you will respond to the world around you. Your genetics is complex as it consists of several interacting factors that influence your health. For example, your genetics have coded information about why some diseases run into your family. Why do some diseases affect only male or females? Why are some people more likely to develop certain diseases than others?
Science behind the knowledge of genetics can help you find out the answers to these questions.
What are Chromosomes and How Do They Work?
DNA is code of life that takes the shape of a coil to form chromosomes. Chromosomes contain DNA in fragmented form known as Genes. There are typically 46 chromosomes found in human cells but are present in the form of 23 p[airs. So, chromosomes are actually compacted packages of DNA. However, the chromosomes are not the structures that can move freely in human or other organism’s cells. They are enclosed in a compact structure, known as nucleus.
DNA has complete instructions about maintaining and creating a life. Therefore each organism has a different number of sets. According to studies, ferns are the organisms that have the largest number of chromosomes i.e. 100 chromosomes and Myrmecia pilosula exist with the most minimum number of chromosomes i.e only 1.
Are all Chromosomes Same?
Each chromosome has specific information related to functioning and maintenance of your life. That’s why all chromosomes are not the same in structure and function.
When you study human chromosomes, you may get to know that there are 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of which 22 are autosomal while the remaining one is called sex chromosome. This 23rd chromosome is different for male and female sex.
In case of males, the 23rd chromosome pair consists of X and Y chromosomes in paired form while in females the pair contain two X (XX) chromosomes.
A DNA molecule is formed of a long length strand that further adopts the shape of chromosomes. Chromosomes are further divided to form new cells. But the amazing thing is that both newly framed cells have the same number and formation of chromosomes as in the parent cell. Thus, this means before division of cells, all the genetic material is copied in a parent cell.
DNA is a double helix spiral strand like a staircase. It is mainly located in the nucleus of the cell where it wraps the special proteins called histones and converts itself onto a unique genetic structure called nucleosome. Around 40 trillion cells are present in your body and the nucleus is found at the center of each cell. The nucleus has the DNA and chromosomes which contain all information of your body and life. The information exists in the form of codes that are called blueprints for life.
A single strand of DNA is approximately 2 meters long. With the help of chromosomes the entire genetic material gets packed in this compact space. The system makes it possible that each new cell gets a complete copy of the genetic material. This is the way humans pass on their genetic information in the form of characteristics from one generation to the next.
How Genes Influence You and Your Life?
DNA segments on chromosomes are known as genes that usually code for specific proteins. The proteins are specified for various functions in your body and also work to determine various traits like hair color, eye color, height and intelligence.
This is the form where genes express themselves by translating a DNA code within a gene. The environmental factors also affect gene expressions. There are approximately 20, 000 coding genes in your bid. However some types of chromosomes can have more than it.
Research also claimed that a great percentage of human DNA doesn’t have a code for anything. The included fragments of DNA are called introns. They do not have a protein code but help regulate the depression of genes. Another type of genetic material known as intergenic DNA have segments of DNA on your chromosomes that do not act like genes. They just promote gene expression in different ways.
ALSO READ: https://onlinehealthpoint.com/how-to-boost-serotonin-naturally-and-without-medication/
The Difference between Autosomal and Sex Chromosomes
As discussed earlier, scientists have categorized 23 pairs of human chromosomes as autosomal and sex chromosomes. The first 22 pairs are called autosomal while the last pair is sex called sex chromosomes.
Autosomal pairs have homologous chromosomes in each pair, having the same code of genes as the patient had. Sometimes, one of these copies of a parent ‘s choice becomes more dominant and expresses itself more than the other.
On the other hand, the pair of sex chromosomes have two different chromosomes in pairs called X and Y chromosomes. The chromosome coming from the parent eggshell is always X and the other from the second parent cell may be X or Y.
Having both XX chromosomes in the 23rd pair of chromosomes conforms to your identity as female while presence of XY chromosomes in the last pair ensures your identity as male. Other than these two combinations may occur in case of some gene mutations.
X and Y are non-homologous chromosomes as the Y is shorter than the X chromosome and has a small number of genes located on it.
Contribution of Genetics and Chromosomes in Your Health
Your health depends on your genetics as your genetics decide your traits and health conditions. It has all the coded information about how your cells will function and how you can respond to the stimuli present around you.
Awesome important ways your genetics use to contribute to your health include:
Inherited Genetic Conditions: The genetic conditions are inherited from the parents. You have them from birth. For example, a genetic mutation at the time of birth causes a genetic condition familial Alzheimer’s disease throughout family members.
Alcohol and Tobacco Consumption: Genetics have an influence on the use of alcohol or tobacco. That impacts your overall health.
Response to Medications: Genes also have effects on the ways your body responds to certain medications and metabolic activities. That directly affects your health.
Risk of Conditions: Certain health conditions including some cancers, type 2 diabetes and heart disease are inherited. Genetics influence the risk of developing the symptoms of inherited diseases. Sometimes, genes also help overcome the severity of some diseases. For example, people who have sickle cell anemia traits also have lower risk of malaria and dengue.
Response to Health Conditions: Your genetics controls how much a disease can harm you and how your body may respond to an infection invasion.
In other words, your chromosomes and genes continue to change slightly throughout your life. The environmental factors and behaviors cause such changes. The phenomenon is known as epigenetics and is considered a natural part of aging.
Which Genetic Conditions are Linked to Which Chromosomes?
Traits and health conditions are often polygenic. They usually result from the complex interaction between several genes. Beside this, environmental factors also contribute. However, mutation in genes on specific chromosomes is the greatest possible cause for significant health conditions.
Monogenic Disorders
Mutation in specific genes can cause slime inherited conditions called monogenic disorders. Important examples include:
| Condition | Chromosomes |
| Sickle cell anemia | 11 |
| Hemophilia | X |
| Alpha thalassemia | 16 |
| Beta thalassemia | 11 |
| Tay Sachs disease | 15 |
| Duchenne muscular dystrophy | X |
| Cystic fibrosis | 7 |
Trisomies
Error in cell division causes the addition of an extra chromosome. This means there are three copies of chromosomes instead of two in each pair. Sometimes these trisomies prove fatal but sometimes they are found in people for lifetime without causing harm. For example:
| Condition | Extra Chromosomes |
| Edward syndrome | 18 |
| Patau syndrome | 23 |
| Down syndrome | 21 |
Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies
The condition occurs due to absence of typical numbers of chromosomes, such as:
| Condition | Karyotype Sex Chromosome |
| Turner syndrome | X |
| Klinefelter syndrome | XXXXY, XXXY, or most commonly XXY |
| XYY syndrome | XYY |
| Triple X syndrome | XXX |
Types of DNA
Location and function of DNA help[s you to categorize the different types of DNA. As the whole genetic material stays in the nucleus, it is easy for you to identify the other type of DNA. The most common one is mitochondrial DNA. As the name suggests, it is located in mitochondria, the specific organelles considered as the power generating station in a cell. It consists of around 15,000 base pairs. Its structure is in the form of a double strand of a coiled spiral that is enclosed around itself. That’s why you find it in round shape. It performs its function within mitochondria with the help of around 40 genes found in it as code for proteins.
However, the nuclear DNA on the other hand, can be clearly differentiated between two types i.e. coding DNA and Non-coding DNA.
Coding DNA
The specific regions within the DNA sequence where coding DNA is found easily is known as genes. Thus genes are the exact points which contain coding DNA , having all the information to form the other types of molecules known as proteins that can help performing different body functions, like:
Enzymes: Special types of proteins contribute in catalyzing the biochemical reactions within the cell.
Transcription Factor: Special proteins that help regulate functions of other genes.
Structural Proteins: Special type of molecules that help form certain structural parts in organisms along with taking part in carrying out different functions in the organism’s body.
Non-Coding DNA
It will surprise you that 99% of your whole genome is formed of non-coding DNA. However, it doesn’t mean that non-coding refers to non-function. Non-coding simply means this type of DNA doesn’t take part in protein formation but performs various functions including DNA packaging and activating the genes.
Environmental Factors Affecting Gene Impression
In general genotype refers to s trait. Its all faculties are considered as multi-factorial. That’s why genetics contributes a lot in determining the traits. However, some external factors including environmental factors, diet, exercise and smoking can affect the way in which the trade waits display themselves.
So, this is the only one percent coding-DNA that makes you unique in this world. The remaining 99% data is the same for all. Therefore, the traitors decide who will be better at some sports or who will have a sweet tooth. A small percentage makes these differences clear between all organisms. This may also make you astonished that when you become able to read all the genetic coding within yourself, you can learn many facts about yourself, such as which type of meal will excite your taste buds, which color of hair you will have or what percentage of intelligence you enjoy. But it is true that reaching that point needs more and more research.
ALSO READ: https://onlinehealthpoint.com/9-potential-physical-and-mental-health-benefits-of-pets/
Conclusion
Your chromosomes, genetics and DNA store all the necessary information about your life in the form of codes. DNA also prepares its copies during cell replication so that that information can be transferred to relevant parts of the body.
Different segments of DNA are also known as genes that actually help determine the traits associated with your physical appearance and internal body condition. This means, chromosomes, genetics and DNA have a great influence on your health.
However, the environmental features affect your genes throughout life and bring changes in them. This article may help you better understand how chromosomes, genes and DNA work to define properly who you are.